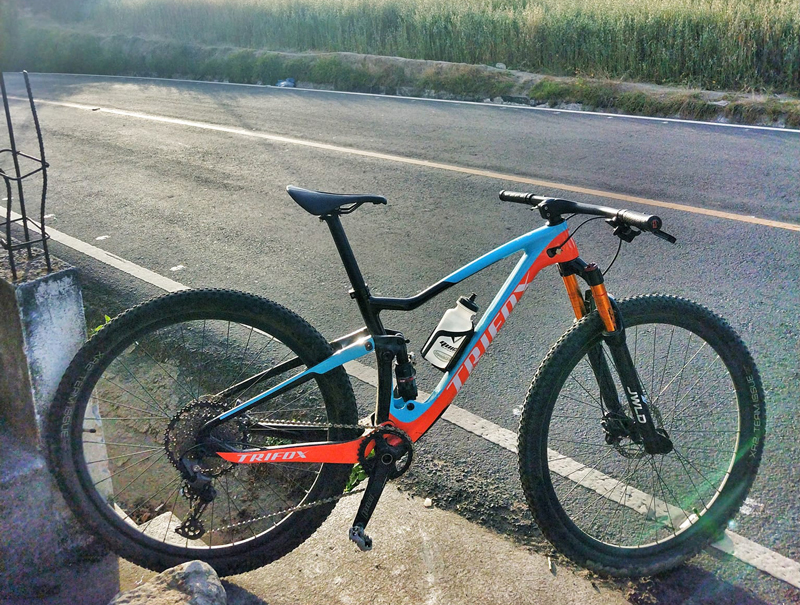

Mountain biking offers a unique experience for those who enjoy the thrill of the outdoors, the rush of speed, and the satisfaction of exploring new terrain. But for 1.70m tall riders, getting the perfect mountain bike can be a daunting task. That's why we've done the research for you and recommend Trifox mountain bike frames as the ultimate choice for all levels of mountain biking enthusiasts who are of average height. 1. Trifox Mountain Bike Frames: The Perfect Match for 1.70m Tall Riders Trifox Mountain Bike Frames are a great choice for 1.70m height as they are made with high-quality carbon fiber material and designed with a unique geometry that offers a comfortable, efficient, and responsive ride. The frames have various features that are perfect for riders of this height - including their lightweight construction, efficient power transfer, and precise handling. 2. Why Trifox Mountain Bike Frames Stand Out Trifox understands the different needs of mountain bikers, and they design their frames to deliver exceptional performance. The frames are built with an emphasis on speed, durability, and stability, all while being featherlight. The frames have a slightly suspended design with an upward curve, allowing for plenty of clearance for 1.70m riders while still providing ample control and precision. 3. Which Trifox Mountain Bike Frame Is Best for 1.70m Tall Riders? Trifox offers a range of mountain bike frames to choose from, and each is designed with distinct specifications to meet the unique needs of different riders. We recommend the Trifox Carbon MTB Frame, which is not only affordable but perfect for 1.70m riders. The frame is made of high-quality carbon fiber, making it ultra-lightweight without sacrificing strength and durability. The frame is also designed with a tapered head tube, which enhances handling and control. 4. Additional Features of the Trifox Carbon MTB Frame Apart from its lightweight carbon fiber construction and tapered head tube, the Trifox Carbon MTB Frame has an advanced suspension system that maximizes performance and reduces fatigue. With a compact and ergonomic design, it provides ample clearance and stability for 1.70m tall riders while still allowing for free and comfortable movement. The frame's aesthetic appeal is also worth mentioning as it's sleek, modern, and visually appealing. 5. Why Trifox Is the Best Choice for 1.70m Tall Riders Trifox is an exceptional brand that has established a solid reputation in the cycling industry for designing quality mountain bike frames. The brand's commitment to producing high-quality products that provide an excellent riding experience is evident in the Trifox Carbon MTB Frame. For 1.70m tall riders, this frame makes the perfect balance of weight, durability, and agility, ultimately enhancing your overall riding experience. If you're a 1.70m tall rider looking for a mountain bike frame that's efficient, lightweight, and comfortable to ride, the Trifox Carbon MTB Frame should be top of your list. With its advanced suspension system, aesthetic appeal, and high-quality carbon fiber material, it offers the best performance for riders of this height. Whether you're an experienced or novice rider, Trifox delivers the best in terms of durability, agility, speed, and overall riding experience. Get your Trifox frame, take your biking experience to the next level, and explore the great outdoors with ease.

As a cyclist, you know the importance of maintaining your bike's tire pressure. One way to ensure that your tires are inflated to the right level is by checking your valve stems. However, if you're not sure how long your valve stems should be, you're not alone. 1. Know Your Rim Profile The first thing to consider when choosing valve stem length is your rim profile. The valve stem should be long enough to reach the base of the rim, but not so long that it is prone to bending or breaking. If you have deep section wheels, you'll need a valve stem with a longer extension than if you have shallow section rims. 2. Consider Your Tire Width The width of your tire is another important factor in determining valve stem length. If you have wider tires, you'll need a longer valve stem to make it easy to access the valve for inflation and deflation. Conversely, if you have a narrow tire, a shorter valve stem can work well. 3. Take Your Valve Type into Account Valve type is another critical factor to consider when choosing valve stem length. There are two main types of valve stems: Presta and Schrader. Schrader valves are typically found on mountain bikes, while Presta valves are commonly found on road bikes. Schrader valves have a wider diameter than Presta valves, so you'll need a longer stem if you have a Schrader valve. 4. Get the Best Fit with Measuring Tools If you're still uncertain about the correct valve stem length for your bike, one way to determine the perfect fit is by using measuring tools. Use a caliper or ruler to measure the distance from the rim bed to the top of the valve hole, and add 10 millimeters to that measurement. This gives you the minimum length of valve stem you need to buy. In conclusion, selecting the right valve stem length for your bike is essential for maintaining the correct tire pressure. To find the perfect length, you should consider your rim profile, tire width, valve type, and use measuring tools to get an accurate fit. It may take some trial and error to find the right valve stem length, but once you do, you'll be able to keep your bike's tires inflated and running smoothly.

Tubeless rims on your road bike can provide excellent performance and comfort advantages over traditional tubed tires. But, setting up tubeless rims requires proper preparation and installation. One of the critical components of the entire setup is taping. Applying the tape correctly to the rim is crucial to prevent air loss and accommodate the tubeless tire. Step 1: Remove Your Old Tape. The first step in replacing your tubeless rim tape is removing the old tape from your rim. You can use a flat tool or a screwdriver to pry up and remove the old tape carefully. Be sure to clean the rim sidewalls and spoke holes thoroughly before installing the new tape. Step 2: Measure Your Rim. Measuring the rim diameter is key to choosing the right size tape for your rim. Check your rim specification or measure the rim diameter with a tape measure. Choose a tape that fits the rim diameter precisely, leaving a bit of an overlap for the seam or valve opening. Step 3: Start Taping. Start your taping by fixing the end of the tape inside the rim bed. Press down the tape firmly to stick it to the bed. Then, slowly and evenly wrap the tape around your rim bed. Take care to avoid wrinkling and overlapping the tape edges. Stretch the tape to get it into the rim's edges, but don't overstretch to prevent tearing or wrinkling. Step 4: Seal The Edges. Sealing the edges of the tape is crucial to prevent air or moisture from leaking through. You can use a small piece of tape or a thin strip of rubber material to seal the edges of the tape. Secure the seal by pressing on it firmly, above the valve opening, and around the rim's edges. Step 5: Trim The Excess. After finishing taping and sealing, trim off excess tape around the rim's edges to achieve a clean and smooth finish. Use a sharp scissors or a razor blade to cut off the excess. Take care not to cut the sealing material you've just applied. Your tubeless rim is now ready to go. Taping tubeless rims on your road bike is an essential part of the entire tubeless tire installation process. With the right tools, careful preparation, and attention to detail, you can tape your tubeless rims correctly and avoid flat tires or air loss. Always remember to remove the old tape, measure the rim diameter, start the taping accurately, seal the edges correctly, and trim the excess to achieve a clean and smooth finish. Happy cycling on your newly tubeless road bike rims!

Cycling is a great way to improve your fitness and overall health. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced rider, you may be looking for ways to enhance your cycling performance. Bike aerodynamics is one of the key factors that can help you achieve your goals. Aerodynamics is the study of how air flows around an object. In cycling, aerodynamics refers to the ability of a bike to cut through the air without creating too much resistance. This is important because the less resistance your bike encounters, the faster and more efficiently you can ride. One way to improve your bike's aerodynamics is to invest in an aero bike frame. For example, Trifox offers carbon road bike frames that are designed for speed and efficiency. These frames are lightweight and have a streamlined shape that minimizes drag. Another way to enhance your cycling performance is to optimize your riding position. This involves adjusting your body position on the bike to reduce wind resistance. The most important factor in achieving an optimal riding position is bike fit. To achieve a proper bike fit, consult a professional bike fitter who can help you adjust your saddle height, handlebar height, and reach. With the right bike fit, you can reduce your frontal area and improve your aerodynamics. In addition to investing in an aero bike frame and optimizing your riding position, there are other factors that can affect your bike aerodynamics. One of the most important is clothing. Wearing tight-fitting, aerodynamic clothing can help reduce drag and improve your cycling performance. Look for cycling-specific clothing that is designed to be aerodynamic and lightweight. Another important factor is wheel selection. Deep section wheels are more aerodynamic than standard wheels, but they can also be heavier. Consider your riding conditions and personal preferences when selecting wheels. Another way to improve your bike aero is to use aerodynamic accessories. These include items such as aerodynamic helmets, water bottles, and even shoe covers. These accessories are designed to reduce drag and improve your speed. However, keep in mind that some accessories may compromise comfort. For example, an aerodynamic helmet may not be as comfortable as a regular helmet, so test out different options before committing to an accessory. In conclusion, there are various ways to enhance your cycling performance through bike aerodynamics. Investing in an aero bike frame, optimizing your riding position, selecting aerodynamic clothing and wheels, and using aerodynamic accessories are all strategies that can help you ride faster and more efficiently. However, keep in mind that improving your aerodynamics requires a balance between speed and comfort. Find the right mix of aerodynamic features that fit your personal preferences and riding style. Happy cycling!

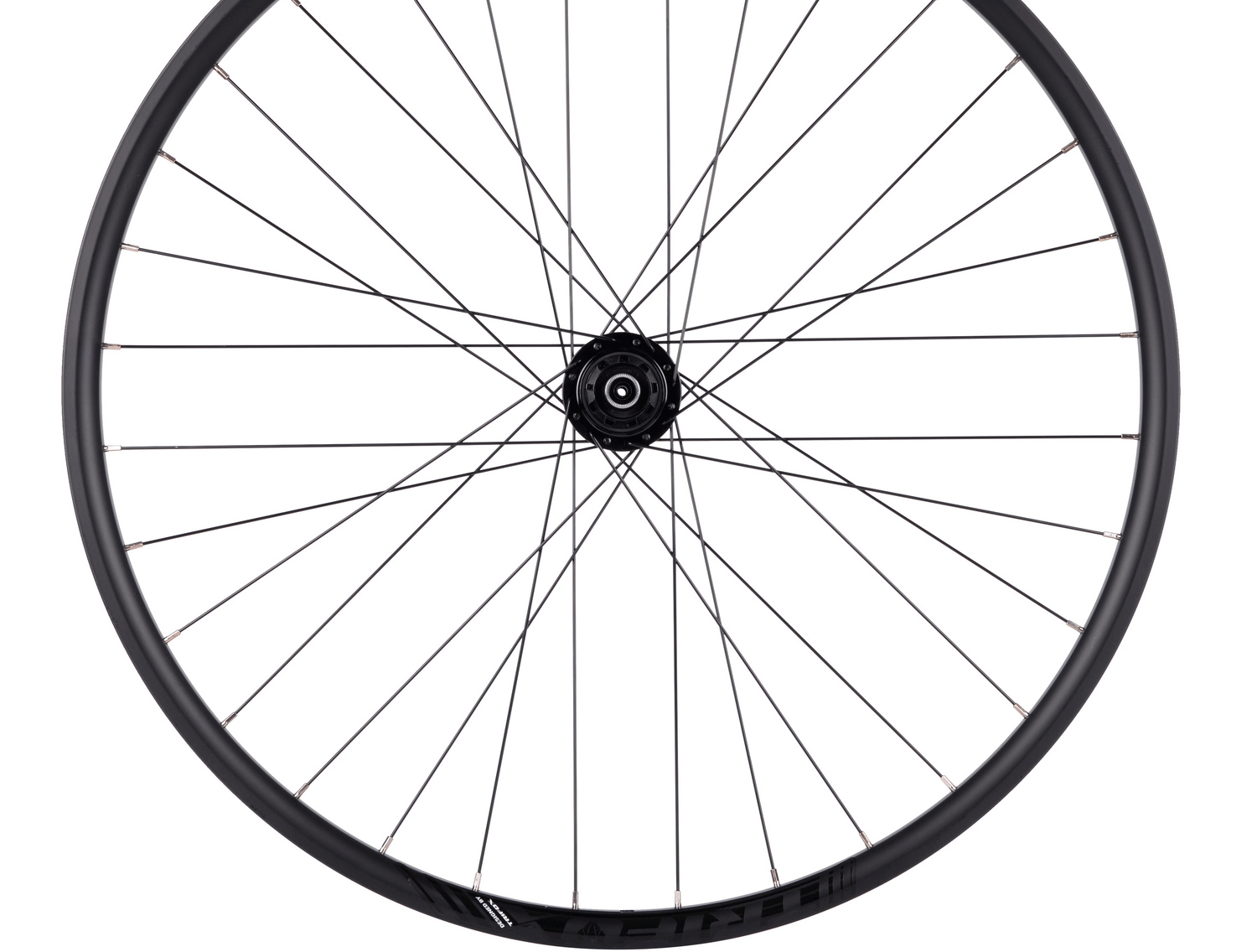
When it comes to bicycles, even the smallest components play a huge role in determining performance. One such component that often goes unnoticed but has a significant impact on both stability and efficiency is the bicycle hub. 1. Enhancing Strength and Durability: Hubs with different spoke numbers offer varying degrees of strength and durability. By increasing the spoke count, the hub becomes sturdier and can distribute the load more effectively, especially in challenging terrains or during intensive rides. This means fewer chances of wheel failure or spoke breakage, providing riders with a reliable and long-lasting cycling experience. 2. Improving Power Transfer: A higher spoke count in a hub enables better power transfer from the cyclist to the road. With a larger number of spokes evenly distributing the force applied during pedaling, there is minimal energy loss, resulting in more efficient pedaling and enhanced acceleration. Hubs with higher spoke numbers make uphill climbs feel less strenuous and flat roads more rewarding. 3. Boosting Stability and Control: Hubs with different spoke numbers contribute to increased stability and control on various surfaces. A hub with a higher spoke count enhances stiffness, reducing flex under heavy loads or high-speed maneuvers. This improved stiffness translates to better handling, responsiveness, and cornering abilities, giving cyclists the confidence to push their limits without compromising safety. 4. Enhancing Aerodynamics: For those cyclists seeking every possible advantage in aerodynamics, hubs with lower spoke numbers are a game-changer. Fewer spokes mean reduced wind resistance, allowing for smoother airflow around the wheels. The decreased drag enables higher speeds and improved performance, especially in time trials, sprints, or races. So if speed is your game, opt for a hub with a lower spoke count. 5. Customization and Personalization: With hubs available in various spoke numbers, cyclists have the freedom to customize their wheels based on their preferences and riding style. Whether you prioritize strength, speed, or a balance of both, selecting the ideal spoke number allows you to fine-tune your cycling experience. This personalization helps you achieve optimal performance and ensures an enjoyable ride every time. Conclusion: Hubs with different spoke numbers bring a plethora of benefits to the world of cycling. From increasing strength and durability to enhancing power transfer, stability, and aerodynamics, they cater to the diverse needs of cyclists. So, whether you're a recreational rider or a competitive cyclist, it's time to embrace the magic of hubs with different spoke numbers and elevate your cycling game to new heights. Explore the possibilities and witness the positive impact they can have on your cycling experience. Remember, investing in a high-quality hub with the right spoke number that suits your riding style and goals is crucial. Upgrade your bicycle hub today and embark on unforgettable cycling adventures. Happy cycling!

When it comes to maintaining your bicycle's performance, a regular tune-up is essential. A bike tune-up is a comprehensive service that ensures that your bike is safe, efficient, and ready for the road. But What does a bike tune up include? 1. Inspection and Assessment: The first step of a bike tune-up is a thorough inspection and assessment process. This involves checking every part of your bike, including the frame, tires, wheels, brakes, gears, and bearings. A professional mechanic will carefully examine each component to identify any issues that may affect the bike's performance or safety. 2. Cleaning and Lubrication: A clean and well-lubricated bike is crucial for optimal performance. During a tune-up, the bike will be thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt, debris, and any residual grease or oil. After cleaning, appropriate lubrication will be applied to the chain, gears, cables, and other moving parts to ensure smooth and efficient operation. 3. Brake Adjustments: The braking system is one of the most critical safety components on your bike. A tune-up will involve inspecting and adjusting the brakes to ensure proper alignment, pad wear, and cable tension. This process will optimize brake performance, ensuring reliable stopping power and control. 4. Gear Adjustments: Smooth shifting between gears is essential for a comfortable ride. In a bike tune-up, the gear system will be evaluated and adjusted to ensure precise shifting and eliminate any skipping or chain slippage issues. This adjustment may include cable tension, limit screw adjustments, and derailleur alignment. 5. Wheel and Tire Inspection: Wheels and tires play a significant role in your bike's performance and safety. During a tune-up, the mechanic will check for any damage, wear, or misalignment. They will inspect the spokes, true the wheels if necessary, and ensure proper tire inflation. This inspection and maintenance will improve ride quality and reduce the risk of punctures and accidents. 6. Bearing Service: Your bike's bearings enable smooth rotation of various parts, such as the headset, bottom bracket, and hubs. A comprehensive tune-up involves inspecting these bearings for wear, cleaning and regreasing them if needed, and adjusting any loose or tight bearings. This process ensures optimal performance and longevity of your bike's components. Conclusion: A bike tune-up is a necessary maintenance service that keeps your bicycle in top shape. By understanding what a bike tune-up includes, you can ensure that your bike performs at its best while promoting safety and longevity. Remember, regular tune-ups and preventative care are key to a smooth, efficient, and enjoyable ride. So, if your bike is due for a tune-up, don't hesitate to schedule an appointment with a professional bike mechanic today.
Understanding how to read bike tire size is crucial, as it directly affects the performance, safety, and comfort of your cycling experience. 1. Understanding the Basics: Before delving into deciphering bike tire sizes, it's important to grasp the basics. Bike tire sizes typically consist of a series of numbers separated by an 'x' or a '-'. For example, 26 x 1.95 or 700c x 25. 2. Decoding the Numbers: The first number indicates the tire's diameter, commonly expressed in inches or millimeters. In the example 26 x 1.95, the diameter is 26 inches. For road bikes, the diameter may be denoted in millimeters, as in 700c x 25, where 700c is the diameter. 3. Interpreting the Width: The second number represents the width of the tire, again either in inches or millimeters. Continuing with our examples, 1.95 inches and 25 millimeters are the respective widths. The width affects the stability and grip of the bike. 4. Considerations for Different Bike Types: a) Mountain Bikes: Mountain bike tires generally have wider widths, providing increased traction in off-road terrains. The standard wheel size for mountain bikes is 26 inches, but newer models may feature 27.5 inches or 29 inches. b) Road Bikes: Road bike tires are narrower, allowing for reduced rolling resistance on smooth surfaces. The commonly used wheel size for road bikes is 700c, although some variations exist. c) Hybrid and City Bikes: Hybrid and city bike tires usually fall between mountain bike and road bike tires in terms of width. The tire size will vary depending on the specific bike model. 5. Additional Tire Markings: Apart from the size specifications, bike tires often have additional markings indicating the tire's tread pattern, recommended tire pressure, maximum load capacity, and other vital information. Familiarizing yourself with these markings can further enhance your understanding of the tire's capabilities. Conclusion: Being able to read bike tire size is essential for all cyclists, ensuring that you can choose the appropriate tires for your riding style and terrain. By comprehending these size specifications, you can improve your bike's performance, comfort, and safety. Remember to consider the bike type, diameter, and width when selecting new tires. With this comprehensive guide, you are now equipped with the knowledge necessary to confidently interpret bike tire sizes. Happy cycling!

When it comes to off-road cycling, enthusiasts have the option to choose from a range of bikes designed to tackle different terrains. One such option gaining popularity is the full suspension fatbike, which offers a unique combination of features to enhance the riding experience. 1. Enhanced Comfort and Control: The integration of full suspension in fatbikes mitigates the impact of rough terrains. By utilizing a front and rear suspension system, these bikes efficiently absorb shocks, bumps, and vibrations, providing riders with a comfortable and stable ride. Suspension forks help in navigating uneven trails and obstacles by minimizing the impact on the rider's wrists, arms, and upper body. Similarly, rear suspensions enable riders to maintain control and traction, resulting in an improved overall biking experience. 2. Increased Traction and Stability: The wider tires of fatbikes, ranging from 3.8 to 5 inches, coupled with lower tire pressure, offer enhanced traction on various surfaces, be it snow, sand, or rocky terrains. The addition of full suspension further improves stability on unpredictable surfaces, enabling cyclists to confidently tackle challenging landscapes. With an increased grip on the ground, riders can smoothly maneuver corners, descend steep slopes, and navigate tricky trails with reduced risk of slipping or losing control. 3. Handling Difficult Terrain: Full suspension fatbikes excel in conquering challenging terrains. The combination of their wide tires, low pressure, and suspension system allows cyclists to effortlessly glide over obstacles, such as tree roots, rocks, and loose gravel. These bikes are specifically designed to ride in snow and sand, making them ideal choices for off-road adventurers seeking new trails and exploration. The unique design elements ensure optimal traction and keep riders in control, even in adverse conditions. 4. Improved Performance: When it comes to achieving speed and efficiency, full suspension fatbikes are not to be underestimated. While the larger tires may pose challenges on paved surfaces, they excel in off-road situations. The suspension system aids in maintaining momentum by absorbing energy-draining impacts, ensuring a smoother and faster ride. As a result, riders can ride longer and tackle more demanding trails with less fatigue, ultimately enhancing their overall performance. Conclusion: Full suspension fatbikes offer unparalleled comfort, control, and versatility for off-road cycling enthusiasts. Their ability to handle difficult terrain, provide enhanced stability, and improve performance make them a superior option for those seeking an adventure-filled journey. Whether you are tackling snowy trails, sandy dunes, or rocky routes, full suspension fatbikes' unique features will provide an enjoyable and invigorating ride. So, if you are considering investing in a fatbike, opting for one with full suspension could be a game-changer for your biking experience.

1. Lightweight and Agility: One of the key factors in determining a road bike's performance is its weight. Carbon fiber excels in this aspect, as it is exceptionally lightweight while maintaining remarkable strength. Trifox carbon fiber road bikes, for instance, are designed with precision and optimized aerodynamics, resulting in a bike that is agile, responsive, and efficient. 2. Superior Strength and Sturdiness: Although carbon fiber is incredibly lightweight, it does not compromise on strength. Carbon fiber road bikes, such as those offered by Trifox, are known for their remarkable durability even under intense riding conditions. This material's strength ensures that riders can confidently conquer rugged terrains, steep ascents, and speedy descents without fearing structural failures. 3. Excellent Vibration Damping: Road vibrations can negatively impact a rider's comfort and endurance. Carbon fiber possesses inherent vibration-damping capabilities, offering riders a smoother and more comfortable ride by reducing road shocks and vibrations. Trifox carbon fiber road bikes incorporate advanced carbon layup techniques to amplify this characteristic, guaranteeing a plush and pleasant riding experience even during long-distance journeys. 4. Customizability and Flexibility: Carbon fiber allows for versatile customization options, catering to individual preferences and riding styles. Trifox offers a variety of carbon fiber road bike frames with different geometries, allowing riders to choose the frame that suits their body dimensions, riding preferences, and performance goals. This flexibility ensures an optimal fit, enhancing overall efficiency and comfort. 5. Enhanced Efficiency and Speed: The exceptional stiffness-to-weight ratio of carbon fiber road bikes directly contributes to their superior efficiency and speed. Trifox's carbon fiber frames excel in power transfer, enabling riders to convert more energy into forward motion. By minimizing energy loss, these bikes provide an unparalleled riding experience and a competitive edge on the road. In the world of road biking, carbon fiber has firmly established itself as a prime material choice, exemplified by Trifox carbon fiber road bikes. Its combination of lightweight, strength, vibration damping, customization options, and performance-driven characteristics makes carbon fiber the ideal material for road bikes. When searching for a road bike that maximizes performance and comfort, carbon fiber frames should be at the top of the list. Explore the exceptional Trifox carbon fiber road bikes to experience the pinnacle of road biking technology and craftsmanship.

















