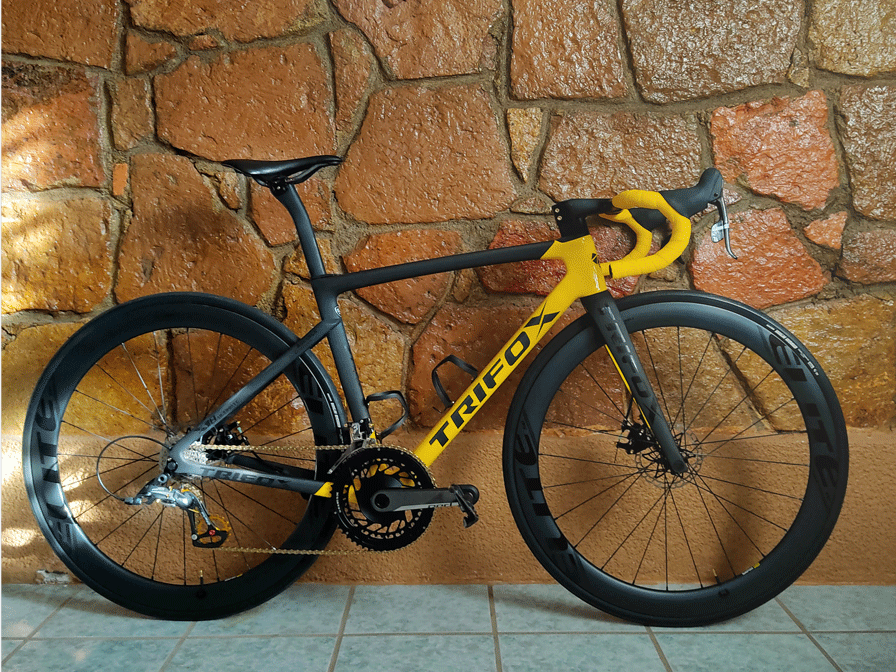
Cycling has evolved significantly over the years, with various bike types catering to different riding styles and terrains. Among these, gravel bikes and road bikes have gained considerable popularity. While they may look similar at first glance, these two types of bikes are designed for distinct purposes and offer unique riding experiences.
1. Purpose and Design Philosophy
Road Bikes
Road bikes are designed primarily for paved surfaces, including city streets and highways. The focus is on speed, efficiency, and aerodynamic performance. They are ideal for long-distance rides, races, and commuting.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bikes, on the other hand, are built to handle a variety of terrains, from smooth pavement to rough gravel roads and trails. They offer versatility and durability, making them suitable for adventure riding, bikepacking, and exploring less-traveled paths.
2. Frame Geometry
Road Bikes
The geometry of a road bike frame is optimized for speed and aerodynamics. It typically features:
Aggressive Riding Position: A lower handlebar height compared to the saddle, promoting an aerodynamic posture.Steeper Angles: The head tube and seat tube angles are steeper, providing quick and responsive handling.Shorter Wheelbase: This results in a more agile bike but can compromise stability on rough terrain.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bike frames are designed for comfort and stability over longer, rougher rides. Key features include:
Relaxed Riding Position: A slightly higher handlebar height relative to the saddle, offering a more upright and comfortable posture;Slacker Angles: The head tube and seat tube angles are slacker than those of road bikes, enhancing stability;Longer Wheelbase: This provides better control and comfort on uneven surfaces and during longer rides.
3. Tire Clearance and Wheel Size
Road Bikes
Road bikes generally use 700c wheels with narrower tires (23-32mm). These tires are designed for low rolling resistance and high pressure, optimizing speed on smooth surfaces. The tire clearance on road bikes is limited to accommodate only narrow tires.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bikes also typically use 700c wheels, but they are compatible with wider tires (35-50mm). Some models can even use 650b wheels for greater versatility. Wider tires provide better traction, comfort, and puncture resistance on rough and uneven surfaces. Gravel bikes feature larger tire clearance to accommodate these wider tires.
4. Suspension and Comfort Features
Road Bikes
Most road bikes do not have suspension systems as they are intended for smooth surfaces. Instead, they rely on a stiff frame and fork to maximize power transfer and speed.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bikes often incorporate comfort-enhancing features such as:
Suspension Forks: Some gravel bikes come with front suspension forks to absorb shocks and vibrations;Thicker Seatposts and Handlebars: Designed to dampen vibrations and improve comfort on rough surfaces;Dropper Seatposts: These allow riders to quickly adjust their saddle height for better control on descents and technical sections.
5. Gearing
Road Bikes
Road bikes feature gearing systems optimized for high-speed riding on flat and rolling terrain. They typically have close-ratio gearing to maintain consistent cadence and power output.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bikes are equipped with a wider range of gears to handle diverse terrains, including steep climbs and loose gravel. They often feature lower gears to make climbing easier and provide better control on technical descents.
6. Handlebar Design
Road Bikes
Road bikes use drop handlebars designed for an aerodynamic riding position. These handlebars have a shallow drop and narrow width, optimizing speed and efficiency.
Gravel Bikes
Gravel bikes also use drop handlebars, but they are often flared and wider. This design provides better control and stability on rough terrain and enhances comfort during long rides.
7. Additional Features
Gravel bikes often come with additional mounts and eyelets for accessories such as fenders, racks, and extra water bottles. This makes them suitable for bikepacking and long-distance touring. Road bikes typically lack these features, focusing instead on minimizing weight and maximizing speed.
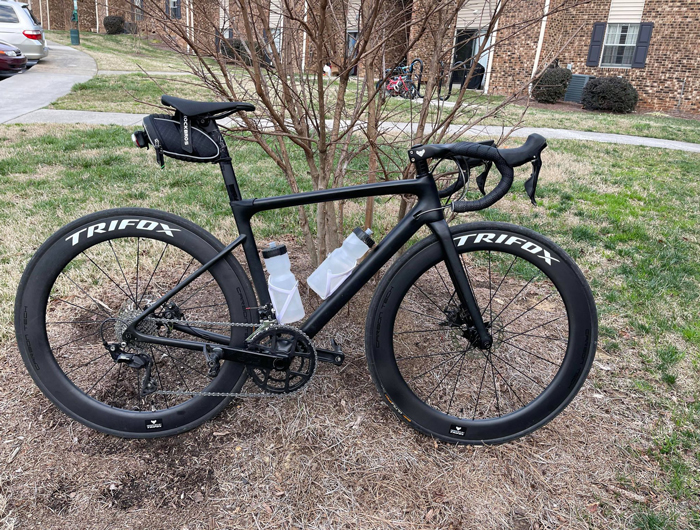

Conclusion
While gravel bikes and road bikes may appear similar, their design philosophies and intended uses set them apart. Road bikes are built for speed and efficiency on paved surfaces, making them perfect for racing and commuting. Gravel bikes, however, offer versatility and durability for a wide range of terrains, making them ideal for adventure riding and exploring off the beaten path.
By understanding these key differences, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right bike for your needs. Whether you're chasing speed on the road or seeking new adventures on gravel paths, there's a perfect bike out there for you.